前言
数据集合来自kaggle
链接:https://www.kaggle.com/c/digit-recognizer/data
其中test和train的csv数据集为所需数据集。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
|
1
|
data = load_breast_cancer()
|
{'data': array([[1.799e+01, 1.038e+01, 1.228e+02, ..., 2.654e-01, 4.601e-01,
1.189e-01],
[2.057e+01, 1.777e+01, 1.329e+02, ..., 1.860e-01, 2.750e-01,
8.902e-02],
[1.969e+01, 2.125e+01, 1.300e+02, ..., 2.430e-01, 3.613e-01,
8.758e-02],
...,
[1.660e+01, 2.808e+01, 1.083e+02, ..., 1.418e-01, 2.218e-01,
7.820e-02],
[2.060e+01, 2.933e+01, 1.401e+02, ..., 2.650e-01, 4.087e-01,
1.240e-01],
[7.760e+00, 2.454e+01, 4.792e+01, ..., 0.000e+00, 2.871e-01,
7.039e-02]]),
'target': array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
'frame': None,
'target_names': array(['malignant', 'benign'], dtype='<U9')
(569, 30)
1
2
|
data.target
#可以看到,乳腺癌数据集有569条记录,30个特征,单看维度虽然不算太高,但是样本量非常少。过拟合的情况可能存在。
|
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1])
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100,random_state=90)
score_pre = cross_val_score(rfc,data.data,data.target,cv=10).mean()#交叉验证的分类默认scoring='accuracy'
score_pre
#这里可以看到,随机森林在乳腺癌数据上的表现本就还不错,在现实数据集上,基本上不可能什么都不调就看到95%以上的准确率
|
0.9648809523809524
n_estimators
在这里选择学习曲线,可以使用网格搜索吗?可以,但是只有学习曲线,才能看见趋势
个人的倾向是,要看见n_estimators在什么取值开始变得平稳,是否一直推动模型整体准确率的上升等信息
第一次的学习曲线,可以先用来帮助我划定范围,我取每十个数作为一个阶段,来观察n_estimators的变化如何
引起模型整体准确率的变化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#####【TIME WARNING: 30 seconds】#####
scorel = []
for i in range(0,200,10):
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=i+1,
n_jobs=-1,
random_state=90)
score = cross_val_score(rfc,data.data,data.target,cv=10).mean()
scorel.append(score)
print(max(scorel),(scorel.index(max(scorel))*10)+1)
plt.figure(figsize=[20,5])
plt.plot(range(1,201,10),scorel)
plt.show()
#list.index([object])
#返回这个object在列表list中的索引
|
0.9631265664160402 71

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
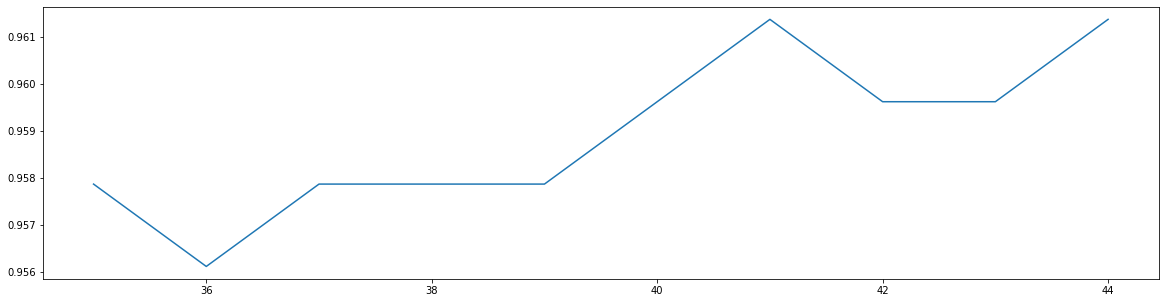
scorel = []
for i in range(35,45):
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=i,
n_jobs=-1,
random_state=90)
score = cross_val_score(rfc,data.data,data.target,cv=10).mean()
scorel.append(score)
print(max(scorel),([*range(35,45)][scorel.index(max(scorel))]))
plt.figure(figsize=[20,5])
plt.plot(range(35,45),scorel)
plt.show()#确定n_estimators为41
|
0.9613721804511279 41

有一些参数是没有参照的,很难说清一个范围,这种情况下我们使用学习曲线,看趋势
从曲线跑出的结果中选取一个更小的区间,再跑曲线
1
2
3
4
5
|
param_grid = {'n_estimators':np.arange(0, 200, 10)}
param_grid = {'max_depth':np.arange(1, 20, 1)}
param_grid = {'max_leaf_nodes':np.arange(25,50,1)}
|
对于大型数据集,可以尝试从1000来构建,先输入1000,每100个叶子一个区间,再逐渐缩小范围
有一些参数是可以找到一个范围的,或者说我们知道他们的取值和随着他们的取值,模型的整体准确率会如何变化,这样的参数我们就可以直接跑网格搜索
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
param_grid = {'criterion':['gini', 'entropy']}
param_grid = {'min_samples_split':np.arange(2, 2+20, 1)}
param_grid = {'min_samples_leaf':np.arange(1, 1+10, 1)}
param_grid = {'max_features':np.arange(5,30,1)}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#调整max_depth
param_grid = {'max_depth':np.arange(1, 20, 1)}
# 一般根据数据的大小来进行一个试探,乳腺癌数据很小,所以可以采用1~10,或者1~20这样的试探
# 但对于像digit recognition那样的大型数据来说,我们应该尝试30~50层深度(或许还不足够
# 更应该画出学习曲线,来观察深度对模型的影响
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
)
GS = GridSearchCV(rfc,param_grid,cv=10)#网格搜索
GS.fit(data.data,data.target)
GS.best_params_#显示调整出来的最佳参数
|
{'max_depth': 8}
1
|
GS.best_score_#返回调整好的最佳参数对应的准确率
|
0.9648809523809524
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#调整max_features
param_grid = {'max_features':np.arange(1,30,1)}
"""
max_features是唯一一个即能够将模型往左(低方差高偏差)推,也能够将模型往右(高方差低偏差)推的参数。我
们需要根据调参前,模型所在的位置(在泛化误差最低点的左边还是右边)来决定我们要将max_features往哪边调。
现在模型位于图像左侧,我们需要的是更高的复杂度,因此我们应该把max_features往更大的方向调整,可用的特征
越多,模型才会越复杂。max_features的默认最小值是sqrt(n_features),因此我们使用这个值作为调参范围的
最小值。
"""
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
)
GS = GridSearchCV(rfc,param_grid,cv=10)
GS.fit(data.data,data.target)
GS.best_params_
|
{'max_features': 7}
0.968421052631579
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
#调整min_samples_leaf
param_grid={'min_samples_leaf':np.arange(1, 1+10, 1)}
#对于min_samples_split和min_samples_leaf,一般是从他们的最小值开始向上增加10或20
#面对高维度高样本量数据,如果不放心,也可以直接+50,对于大型数据,可能需要200~300的范围
#如果调整的时候发现准确率无论如何都上不来,那可以放心大胆调一个很大的数据,大力限制模型的复杂度
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
)
GS = GridSearchCV(rfc,param_grid,cv=10)
GS.fit(data.data,data.target)
GS.best_params_
|
{'min_samples_leaf': 1}
0.9613721804511279
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#调整min_samples_split
param_grid={'min_samples_split':np.arange(2, 2+20, 1)}
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
)
GS = GridSearchCV(rfc,param_grid,cv=10)
GS.fit(data.data,data.target)
GS.best_params_
|
{'min_samples_split': 8}
0.9648809523809524
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#调整Criterion
param_grid = {'criterion':['gini', 'entropy']}
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
)
GS = GridSearchCV(rfc,param_grid,cv=10)
GS.fit(data.data,data.target)
GS.best_params_
|
{'criterion': 'entropy'}
0.9666666666666666
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=41
,random_state=90
,max_depth=8
#,max_features=7
#,min_samples_leaf=4
#,min_samples_split= 8
,criterion= 'entropy'
)
|
1
2
3
|
#rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=39,random_state=90)
score = cross_val_score(rfc,data.data,data.target,cv=10).mean()
score
|
0.9666666666666666
-0.0035087719298244613